The difference between uniqueness and innovation lies in their conceptual focus.
Uniqueness is about being one of a kind or distinct from all others, not necessarily related to change or improvement.
Innovation is specifically concerned with the introduction and practical application of new ideas, products, or processes that aim to improve or add value.
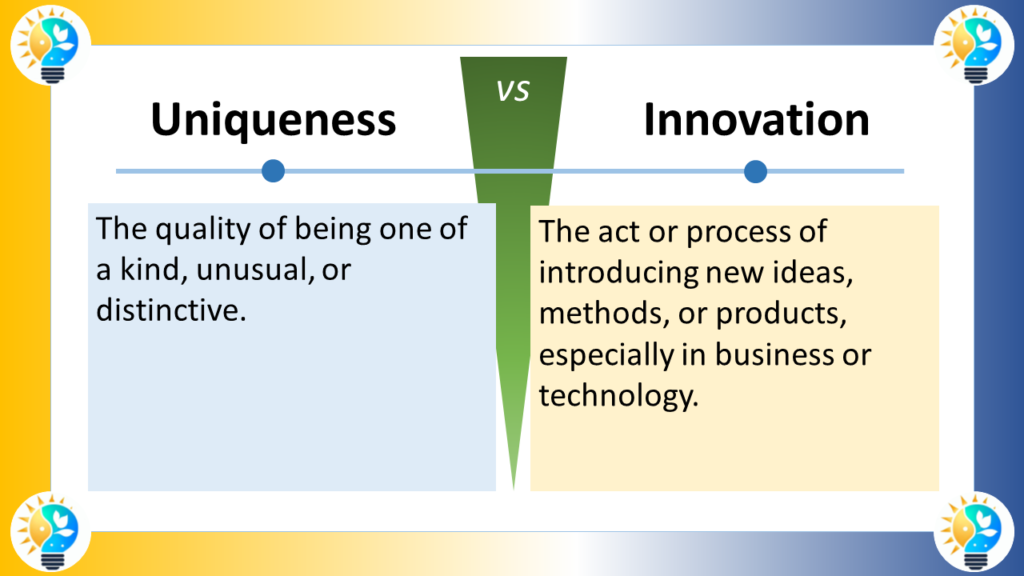
Definition
Uniqueness
Uniqueness refers to the quality of being the only one of its kind; it is about distinctiveness and individuality.
- Characteristics of Uniqueness:
- Singularity: Not replicated or duplicated; stands alone in its characteristics.
- Distinction: Differentiates itself from others based on specific attributes.
- Originality: Often original, but not necessarily associated with functionality or improvement.
Innovation
Innovation is the process of making changes by introducing new methods, ideas, or products that offer better solutions or enhance value.
- Characteristics of Innovation:
- Novelty and Improvement: Introduces new or significantly improved concepts.
- Implementation: Involves the practical application and realization of ideas.
- Value Creation: Aims to address needs, solve problems, or enhance efficiency.
More Synonyms on innovation, innovate and innovative
Innovation Terms

Innovation is considered as a driving force in progress.
It includes the introduction of novel ideas, methods, or products that bring positive change and advancement.
For more information about innovations, check our glossary
Relationship and Relevance
While uniqueness can be an aspect of innovation, not all unique concepts are innovative. Innovation requires not only novelty but also applicability and value generation. A unique idea becomes innovative when it is actionable and fulfills a need or improves upon existing solutions.
The key difference between uniqueness and innovation is:
Uniqueness refers to the quality of being one-of-a-kind, unusual, or unprecedented. It is about creating something that is different or distinct from what already exists.
However, uniqueness alone is not enough for true innovation. As the article states, "Uniqueness Isn't Enough When It Comes to Innovation."
Innovation goes beyond just being unique and requires creating something that is both novel and meaningful or valuable to customers.
The article uses the example of the iPod, which was not the first unique music player device, but became innovative by combining unique features (small size, large storage, sharing capabilities) in a way that was truly meaningful and useful to customers.
So in summary:
- Uniqueness is about creating something different or distinct, but it does not necessarily make something innovative.
- Innovation requires taking uniqueness a step further by creating something that is both new and provides meaningful value or benefits to customers.
The key is not just pursuing uniqueness for its own sake, but ensuring that any unique features or capabilities are truly meaningful and useful to the target customers. This is what transforms uniqueness into true innovation.
Context for Using Each Term
- Uniqueness is often used to describe personal attributes, artworks, experiences, or products that are distinctive due to their inherent qualities.
- Innovation is used in the context of business, science, and technology, emphasizing the process of introducing and implementing new ideas that have practical benefits.
Example of Utilization
A fashion designer might create a unique dress with an unprecedented design that has never been seen before. However, a company that develops a new fabric that is both stronger and more environmentally friendly than existing materials is engaging in innovation because it introduces a new product that offers tangible improvements.
In essence, uniqueness encapsulates the quality of being the only one of its kind, often valued for its distinctiveness, while innovation refers to the process of applying creative and novel ideas that result in meaningful improvements or solutions.
- Uniqueness Isn't Enough When it Comes to Innovation
- What is the Difference Between Originality and Innovation?
- Innovation vs Improvement
- Innovation Trends
- Difference Between Transformation and Innovation
FAQ
Q1: Can something be both unique and innovative?
A1: Yes, an innovation can also be unique if it introduces a novel solution that is unlike anything else available.
Q2: Is uniqueness always valuable?
A2: Not necessarily. Uniqueness can be valuable if it meets a need or desire, but being different for its own sake may not add value.
Q3: Do all innovations need to be unique?
A3: While many innovations are unique in some way, an innovation can build upon existing ideas while still adding new value.
Q4: How do businesses balance uniqueness and innovation?
A4: Businesses often strive to innovate in ways that also create uniqueness, aiming for solutions that are both novel and distinctive.
Q5: Can uniqueness lead to innovation?
A5: Yes, pursuing uniqueness can sometimes lead to innovative approaches or solutions as individuals or organizations seek new ways to differentiate themselves.