The primary difference between experimentation and innovation lies in their purpose and outcome.
Experimentation is the process of testing and trying out new ideas or methods to gain knowledge,
Innovation involves applying new ideas to create valuable and effective changes in products, services, or processes.
Definition
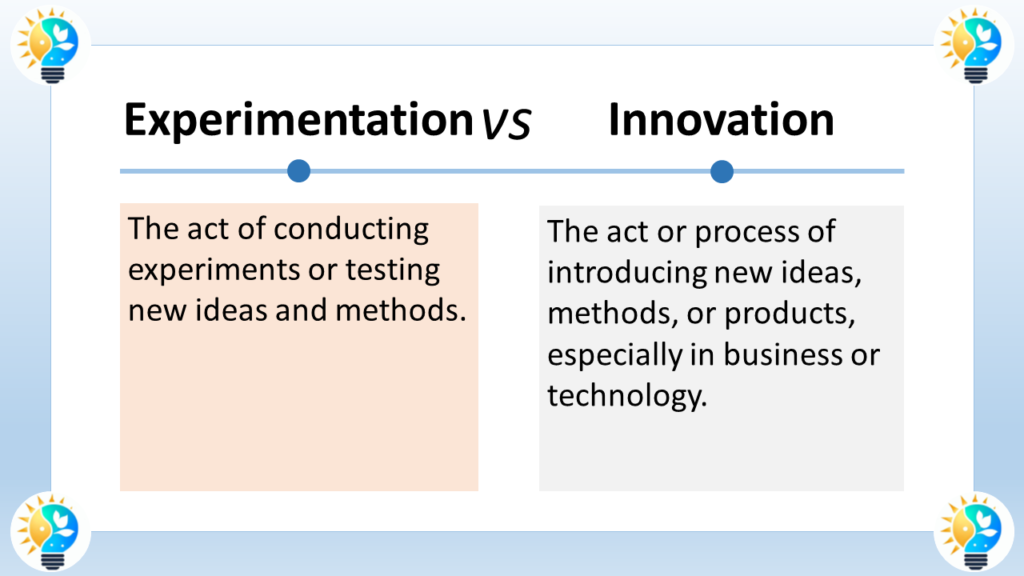
Experimentation
Experimentation is a methodical approach to exploring and evaluating new concepts or hypotheses, often through a process of trial and error.
- Characteristics of Experimentation:
- Inquiry-driven: Aimed at discovering new information or confirming existing theories.
- Controlled Conditions: Involves systematic testing under variable-controlled settings.
- Data Collection: Critical for analyzing results and drawing conclusions.
Innovation
Innovation refers to the practical implementation of new ideas, leading to the creation or improvement of products, services, or processes.
- Characteristics of Innovation:
- Application: Focuses on putting ideas into practice for real-world impact.
- Novelty: Introduces new or significantly improved offerings.
- Value Creation: Generates economic or social value through its implementation.
More Synonyms on innovation, innovate and innovative
Innovation Terms

Innovation is considered as a driving force in progress.
It includes the introduction of novel ideas, methods, or products that bring positive change and advancement.
For more information about innovations, check our glossary
Relationship and Relevance
Experimentation often serves as the foundation for innovation. Through experiments, individuals and organizations can explore the potential of new ideas, which can then be refined and turned into innovative applications. However, while experimentation is about the process of discovery and learning, innovation is about the end result and its implementation in the market or society.
Based on the search results provided, the key differences between experimentation and innovation are:
Experimentation
- Experimentation involves a structured process of testing hypotheses, collecting data, and iterating based on the results.
- It is an evidence-based approach that allows companies to validate ideas and make data-driven decisions, rather than relying on gut feelings or assumptions.
- Experimentation is an essential part of the innovation process, as it helps innovators quickly test and refine new ideas.
- Companies that innovate continuously make experimentation a core part of their business model, running thousands of experiments to find the most successful solutions.
Innovation
- Innovation refers to the creation of something entirely new - a novel product, service, process or business model.
- It involves a more radical, disruptive approach that challenges the status quo and explores uncharted territories.
- Innovation is driven by a desire to do things differently rather than just better, often based on visionary foresight.
- While experimentation supports innovation, it does not necessarily create innovation on its own. There is also a role for intuition, creativity and thinking outside the box.
In summary, experimentation is a critical tool that enables and supports the innovation process, but innovation itself involves the development of truly novel solutions that go beyond just improving existing offerings. The most successful innovators are able to balance experimentation with other creative and visionary approaches.
Context for Using Each Term
- Experimentation should be used when discussing the process of testing ideas or running trials to gather data and insights.
- Innovation should be used when referring to the concrete outcomes of new ideas that have been successfully applied and have brought about change.
Example of Utilization
A tech company that conducts numerous trials to test the feasibility of using augmented reality for educational purposes is engaging in experimentation. When the company develops a new, user-friendly augmented reality platform that transforms the educational experience and becomes widely adopted, it has achieved innovation.
In essence, experimentation is a crucial step in the journey towards innovation, providing the necessary insights and knowledge that enable the leap from idea to impactful application.
FAQ
Q: Is experimentation always necessary for innovation?
A: While not always necessary, experimentation often provides valuable insights that can lead to more successful innovations.
Q: Can innovation occur without prior experimentation?
A: Yes, some innovations may arise from sudden insights or combinations of existing ideas without formal experimentation.
Q: How do experimentation and innovation contribute to progress?
A: Experimentation generates knowledge and validates ideas, while innovation applies this knowledge to create practical solutions and improvements.
Q: Are all experiments aimed at innovation?
A: No, some experiments are conducted purely for scientific understanding or to validate existing theories, without immediate innovative goals.
Q: Can innovation lead to new experiments?
A: Absolutely. Innovations often raise new questions or reveal areas for improvement, prompting further experimentation.