No innovation without innovator! Know all the key synonyms and antonyms of innovators.

Innovation is considered as a driving force in progress.
It includes the introduction of novel ideas, methods, or products that bring positive change and advancement.
For more information about innovations, check our glossary
Definition of Innovators
An innovator is someone who creates or introduces something new, such as a product, service, or idea.
This can involve the practical implementation of new ideas that result in the introduction of new goods or services or the improvement of existing ones[2].
Innovators can be individuals, businesses, or organizations that are driven by a commitment to bring about positive change and progress[3][4].
The term is often associated with entrepreneurship and the ability to recognize needs, gather competent people with relevant technology, and secure financial support to bring about meaningful innovations[2].
Understanding the nuances between Innovation, Innovator, Innovate and Innovative
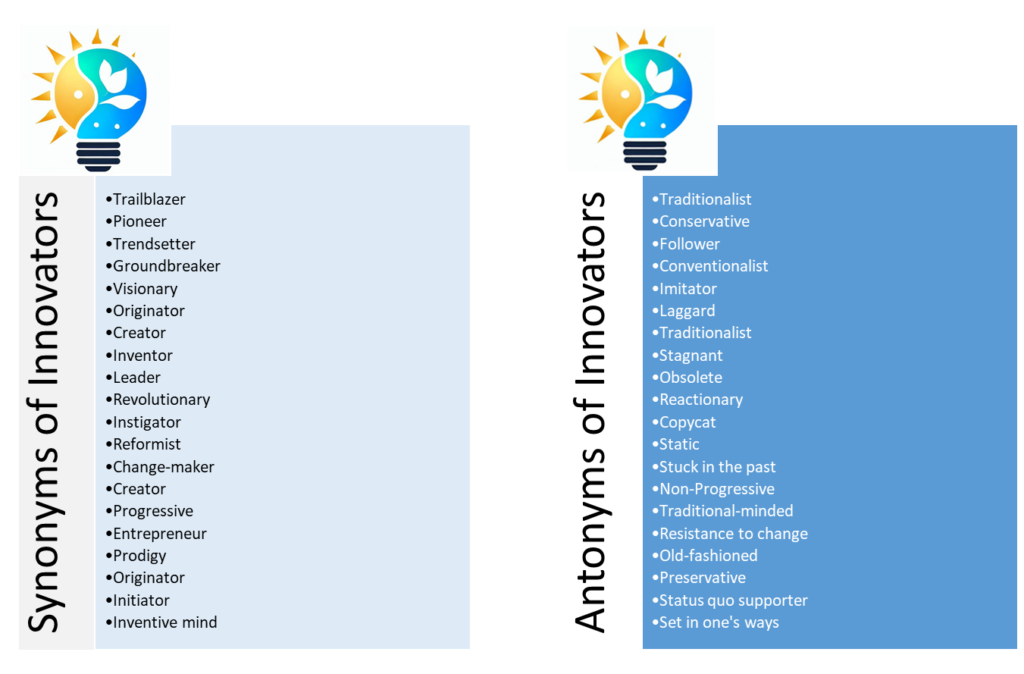
Synonyms of Innovators
- Change-maker: An individual who actively contributes to positive and transformative changes, often in social or environmental contexts.
- Creator: An individual who brings something into existence, whether it be a product, work of art, or concept.
- Entrepreneur: A person who organizes and operates a business, taking on financial risks in the pursuit of new opportunities and innovation.
- Groundbreaker: An individual who introduces new ideas, methods, or technologies, breaking new ground and paving the way for advancements.
- Inventor: Someone who devises and develops a new product, process, or device, typically through creativity and ingenuity.
- Initiator: Someone who starts or sets a process or series of events in motion, often with the aim of achieving a specific goal.
- Instigator: Someone who initiates or provokes a particular action or event, often with the intention of inspiring change.
- Leader: A person who guides or directs others, often by setting an example and inspiring them to achieve common goals.
- Originator: The person who first brings a new concept, idea, or creation into existence.
- Pioneer: Someone who is among the first to explore or settle in a new area, and metaphorically, someone who is at the forefront of new developments or ideas.
- Prodigy: A person, especially a young one, with exceptional abilities or talents in a particular field.
- Progressive: Someone who supports or advocates for innovation, reform, and progress, often in social or political contexts.
- Reformist: A person who advocates for and works towards making gradual improvements or changes, especially in social, political, or economic systems.
- Revolutionary: A person who advocates or supports a significant and radical change, especially in politics or social structures.
- Trailblazer: A person who is a pioneer or innovator, leading the way in a particular field or activity, often creating a path for others to follow.
- Trendsetter: A person or entity that establishes or popularizes a new trend or style, influencing others to follow suit.
- Visionary: Someone with an exceptional ability to imagine or plan the future, often with innovative ideas or insights that go beyond current norms.

Innovation is considered as a driving force in progress.
It includes the introduction of novel ideas, methods, or products that bring positive change and advancement.
For more information about innovations, check our glossary
Antonyms of Innovators
- Copycat: Someone who mimics the ideas, behaviors, or products of others without introducing original or innovative elements.
- Conservative: A person who favors maintaining existing institutions and traditions, and is typically resistant to rapid or radical change.
- Conventionalist: A person who adheres to widely accepted norms, practices, or standards, and is resistant to unconventional or groundbreaking ideas.
- Follower: Someone who imitates or adopts the ideas, behaviors, or trends set by others, rather than initiating or innovating themselves.
- Imitator: Someone who copies or reproduces existing ideas, methods, or products without introducing significant changes or innovations.
- Laggard: A person or entity that is slow to adopt new technologies, ideas, or trends, often trailing behind the majority.
- Obsolete: Outdated or no longer in use, especially regarding ideas, technologies, or practices.
- Old-fashioned: Outdated or no longer in style, often used to describe ideas, practices, or objects that belong to a previous era.
- Preservative: A person or entity that seeks to preserve existing conditions, structures, or practices without promoting change.
- Reactionary: A person who opposes social or political progress and seeks to preserve or revert to traditional values and institutions.
- Stagnant: A person or situation that lacks growth, development, or progress, and is resistant to change.
- Resistance to change: A characteristic indicating an unwillingness or reluctance to embrace new ideas or methods.
- Static: Lacking in movement, development, or progress; resistant to change.
- Stuck in the past: A term used to describe individuals or entities unwilling to embrace new ideas, technologies, or approaches.
- Status quo supporter: Someone who advocates for maintaining the current state of affairs, resisting alterations or innovations.
- Set in one’s ways: Describes a person who is resistant to change, often due to long-standing habits or beliefs.
- Traditionalist: Someone who adheres to and values established customs, practices, or ideas, resisting change or innovation.
- Traditional-minded: A person who tends to favor and maintain established customs, practices, or ways of thinking.
What are the Opposites of Innovation? All the best Antonyms
The Triad of Innovation: Creativity, Curiosity, and Risk-Taking
Creativity: At the heart of innovation lies an unwavering commitment to creativity. Innovators possess the ability to think beyond conventional boundaries, envisioning solutions that others may overlook. Whether it’s reimagining processes, products, or services, a creative mindset is the cornerstone of groundbreaking advancements.
Curiosity: An insatiable curiosity propels innovators forward. Questioning the status quo and constantly seeking new knowledge, innovators are driven by a deep desire to understand, explore, and challenge existing paradigms. This innate curiosity fuels a continuous cycle of learning and adaptation.
Risk-Taking: True innovation often requires stepping into the unknown, and innovators are not averse to risk. They embrace uncertainty, viewing challenges as opportunities rather than obstacles. This willingness to take calculated risks sets innovators apart, allowing them to navigate uncharted territories and bring about transformative change.
What is the opposite of innovator?
Have you ever wondered about the counterpart to the innovator? We review here the opposite profiles of innovator.
Defining the “Opposite” of Innovator
Innovation leaders often focus on nurturing creative thinking and groundbreaking ideas.
But what happens when we shift our perspective to consider the individuals or factors that resist change and innovation? This leads us to the concept of the “opposite” of an innovator.
The opposite of an innovator can take various forms:
1. The Conservator: This individual or group is resistant to change and clings to traditional methods and practices. They often prioritize stability and continuity over innovation.
2. The Naysayer: Naysayers are quick to dismiss new ideas and innovations. They are skeptical and critical, making it challenging for innovative concepts to gain traction.
3. The Status Quo Defender: They oppose any deviation from the established status quo. Even if their actions hinders progress. They may fear the risks associated with change for themselves or their organization.
What are the Opposites of Innovation? All the best Antonyms
Benefits of Oppositions within the Innovation Ecosystem
While it may seem counterintuitive, the presence of opposites within an organization can serve a purpose in the innovation ecosystem:
1. Checks and Balances: Opposition can counterbalance innovators. It ensure that innovation efforts are well-considered and are correctly executed. It also check their alignment with the organization’s overall goals and values.
2. Stress Testing: They challenge innovators to refine and strengthen their ideas. This may lead to more robust and viable innovations.
3. Risk Mitigation: Opposition can help identify potential pitfalls and risks associated with innovation. They may prompt organizations to take a more calculated approach.
Navigating the Interplay
Innovation leaders must navigate the interplay between innovators and their opposition. Here are some strategies for effectively managing this dynamic:
1. Fostering Constructive Dialogue: Encourage open and respectful communication between innovators and their oppositions. It facilitates a healthy exchange of ideas and viewpoints.
2. Creating Cross-Functional Teams: Form interdisciplinary teams that bring together innovators and counterparts. This allow to leverage their diverse perspectives and skills.
3. Setting Clear Goals: Establish clear and shared goals for innovation initiatives. Both sides can then work toward a common purpose.
Embracing the Tension
The tension between innovators and their opposites is not necessarily a negative force. Innovation leaders must harness it to balance the innovation drive.
1. Innovation as an Evolutionary Process: Consider innovation as an ongoing evolutionary process. Both sides contribute to refining and adapting ideas over time.
2. Continuous Learning: Encourage a culture of continuous learning and adaptation. Feedback from opposites informs the innovation process.
3. Inclusive Leadership: Embrace diverse perspectives and fosters collaboration between innovators and opposites.